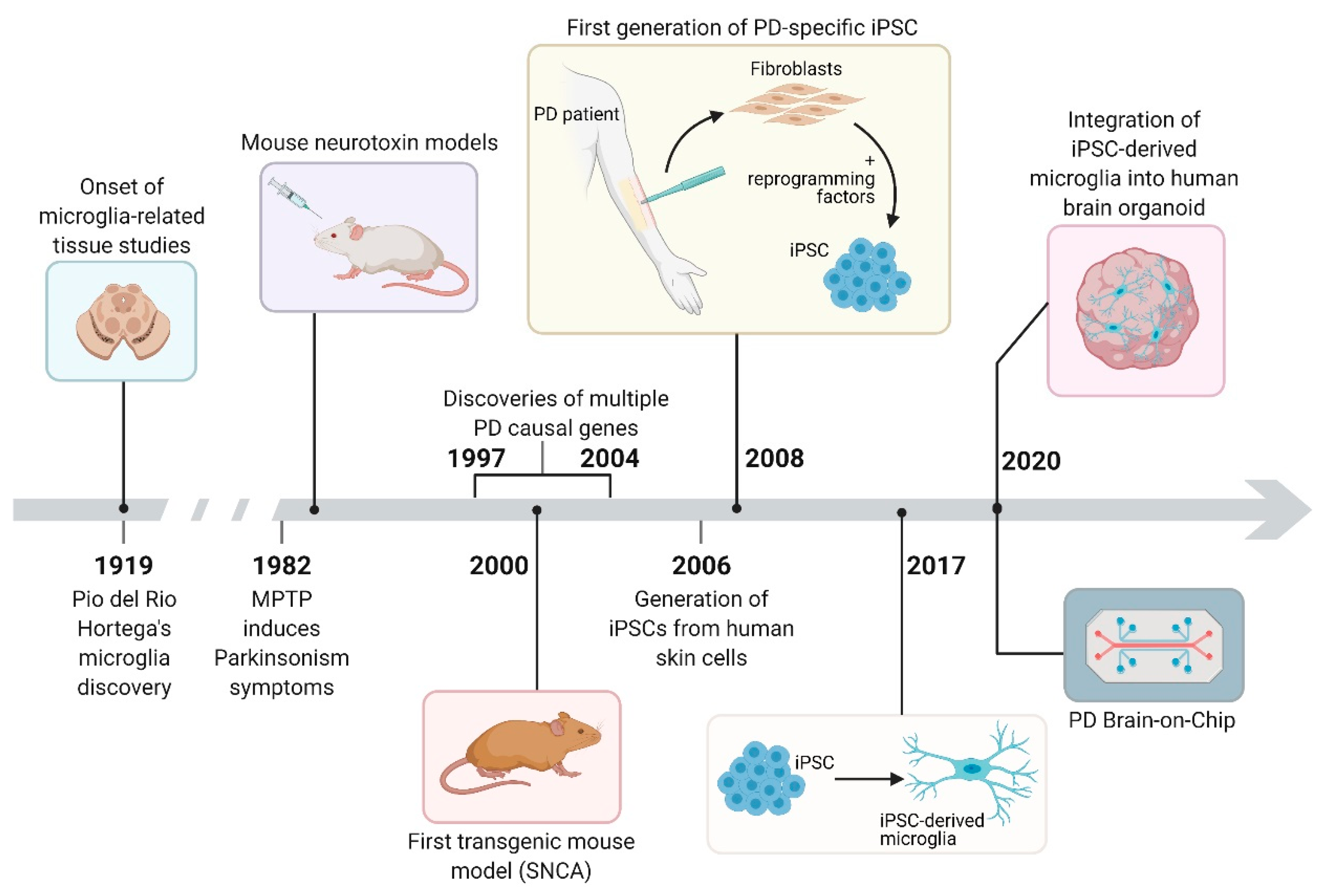
Mechanism of miR-132-3p Promoting Neuroinflammation and Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in Parkinson's Disease | eNeuro

Lipopolysaccharide animal models of Parkinson's disease: Recent progress and relevance to clinical disease - ScienceDirect

Lipopolysaccharide animal models of Parkinson's disease: Recent progress and relevance to clinical disease | Semantic Scholar

PDF) Inflammatory Animal Model for Parkinson's Disease: The Intranigral Injection of LPS Induced the Inflammatory Process along with the Selective Degeneration of Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Galangin Reduces the Loss of Dopaminergic Neurons in an LPS-Evoked Model of Parkinson's Disease in Rats

Novel compound FLZ alleviates rotenone-induced PD mouse model by suppressing TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway through microbiota–gut–brain axis - ScienceDirect
Intranasal LPS-Mediated Parkinson's Model Challenges the Pathogenesis of Nasal Cavity and Environmental Toxins | PLOS ONE

Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide induced model of Parkinson's disease: Role of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation - ScienceDirect
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Further Characterization of Intrastriatal Lipopolysaccharide Model of Parkinson's Disease in C57BL/6 Mice

Pramipexole inhibits astrocytic NLRP3 inflammasome activation via Drd3-dependent autophagy in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease | Acta Pharmacologica Sinica
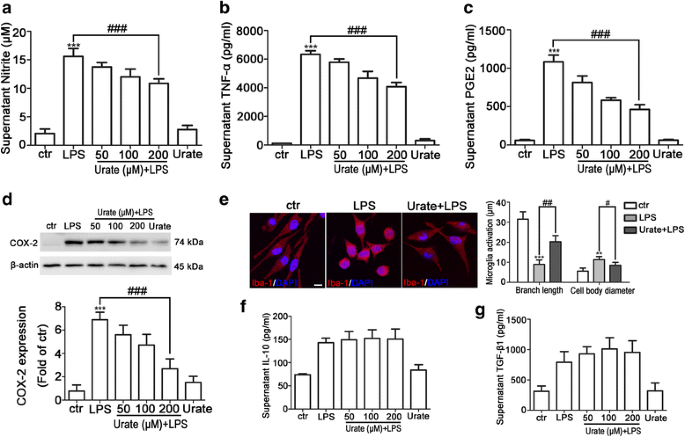
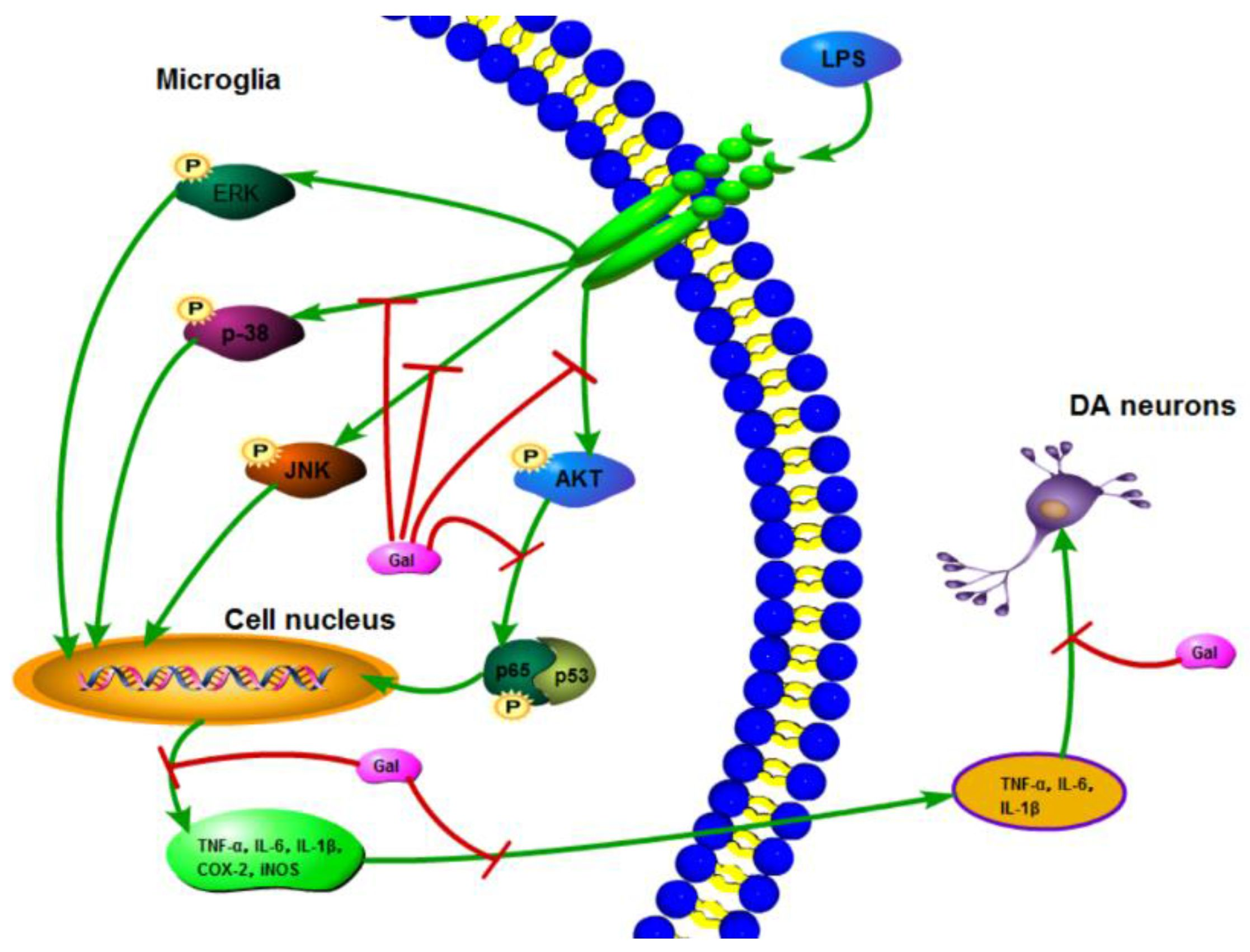
Urate inhibits microglia activation to protect neurons in an LPS-induced model of Parkinson's disease | Journal of Neuroinflammation | Full Text
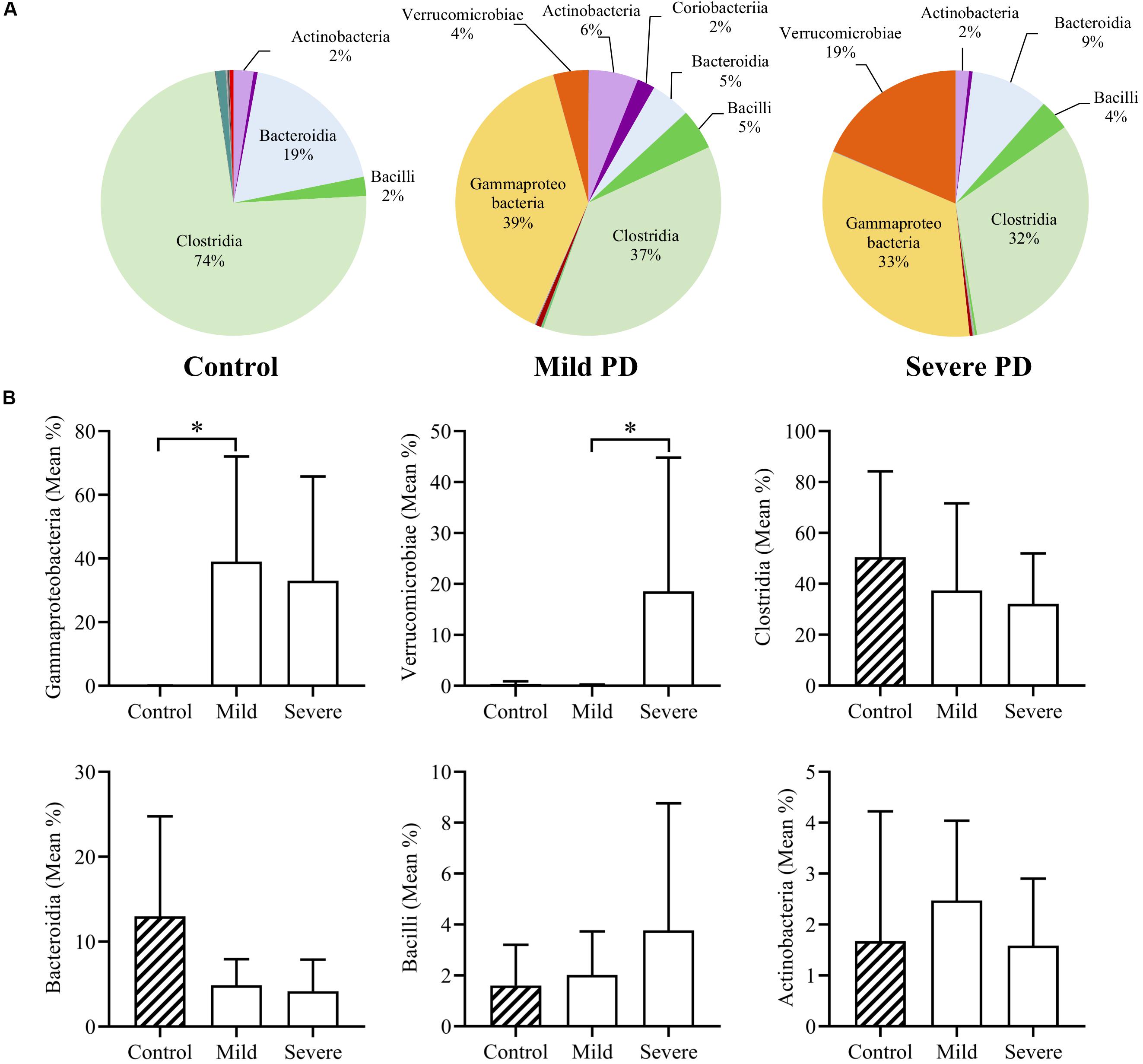
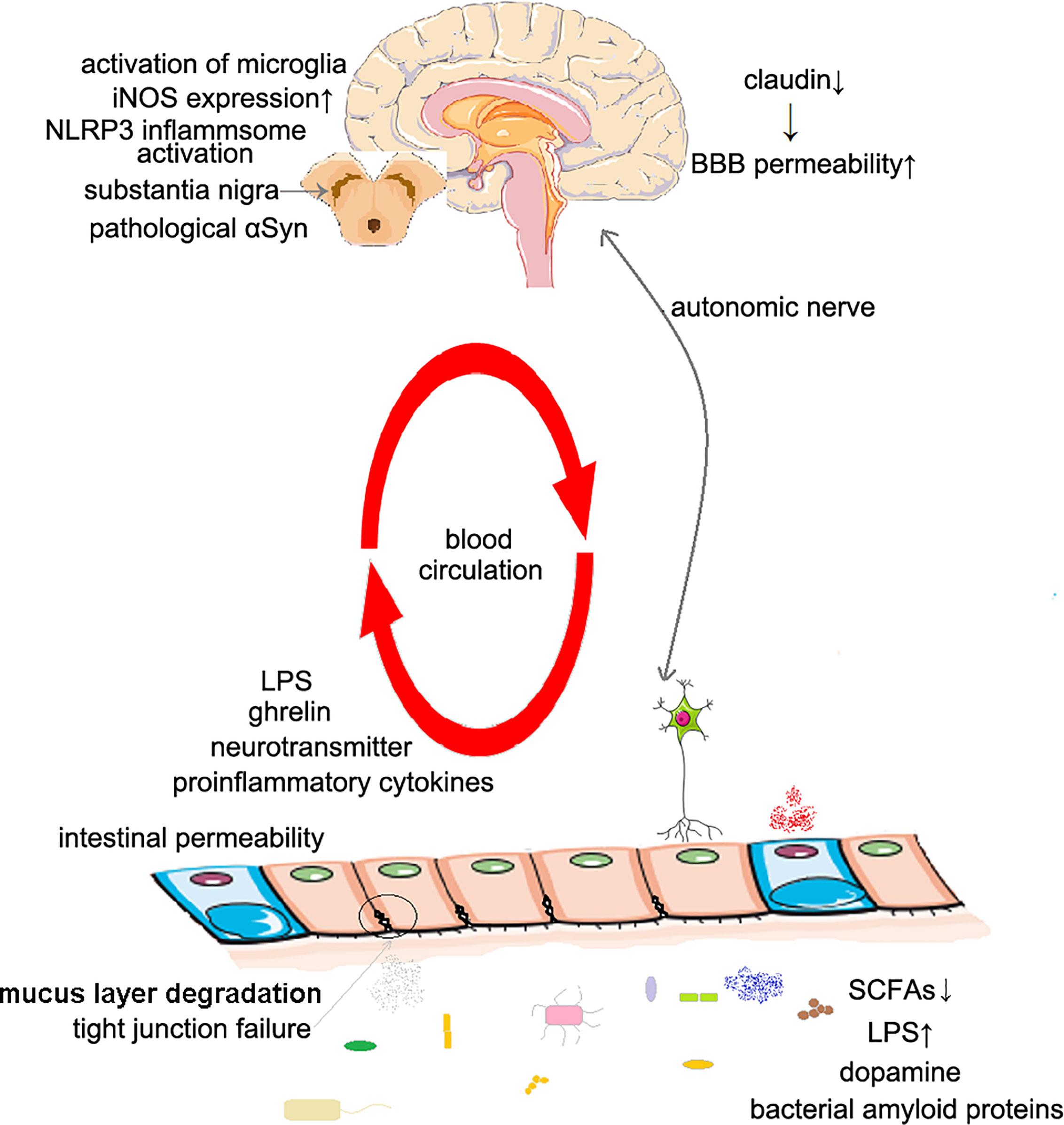
Frontiers | Altered Gut Microbiome in Parkinson's Disease and the Influence of Lipopolysaccharide in a Human α-Synuclein Over-Expressing Mouse Model
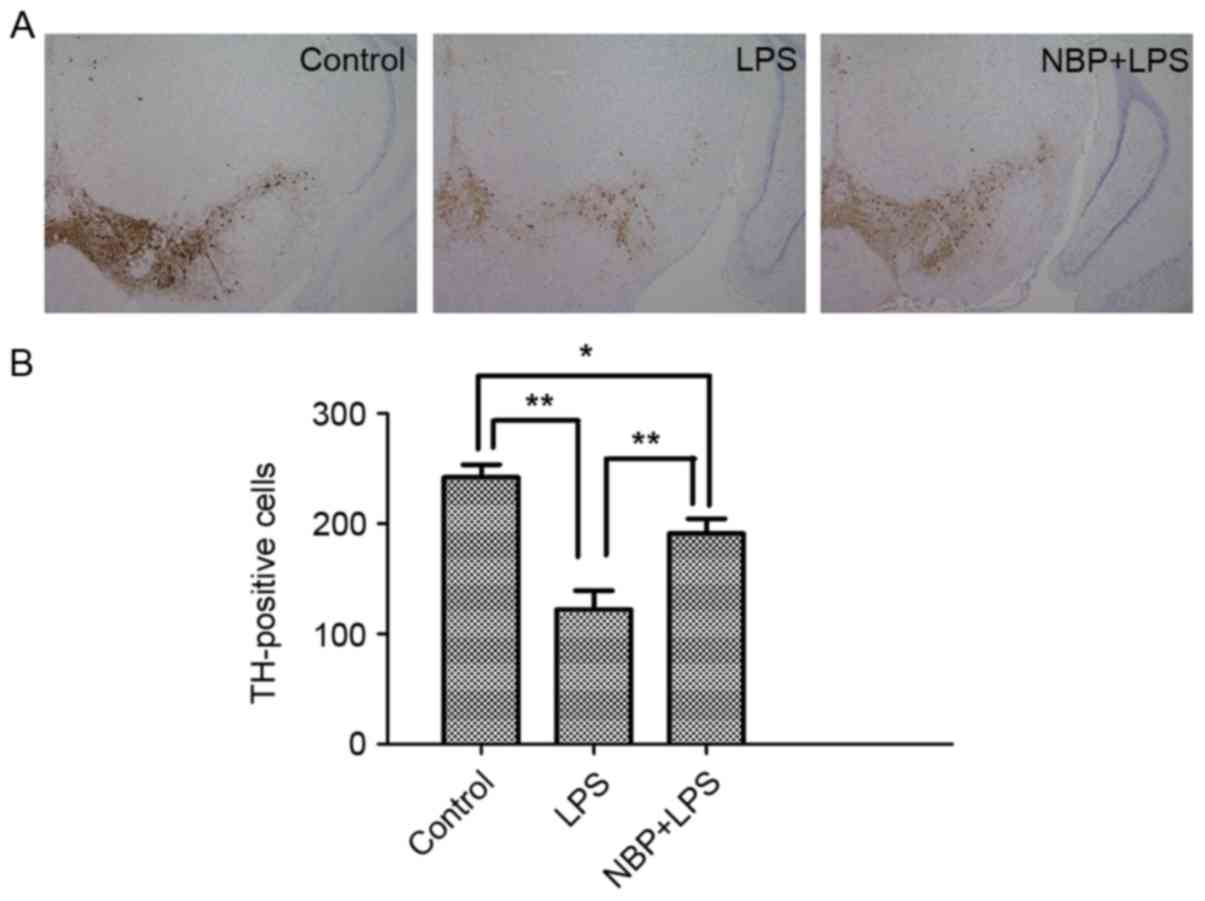
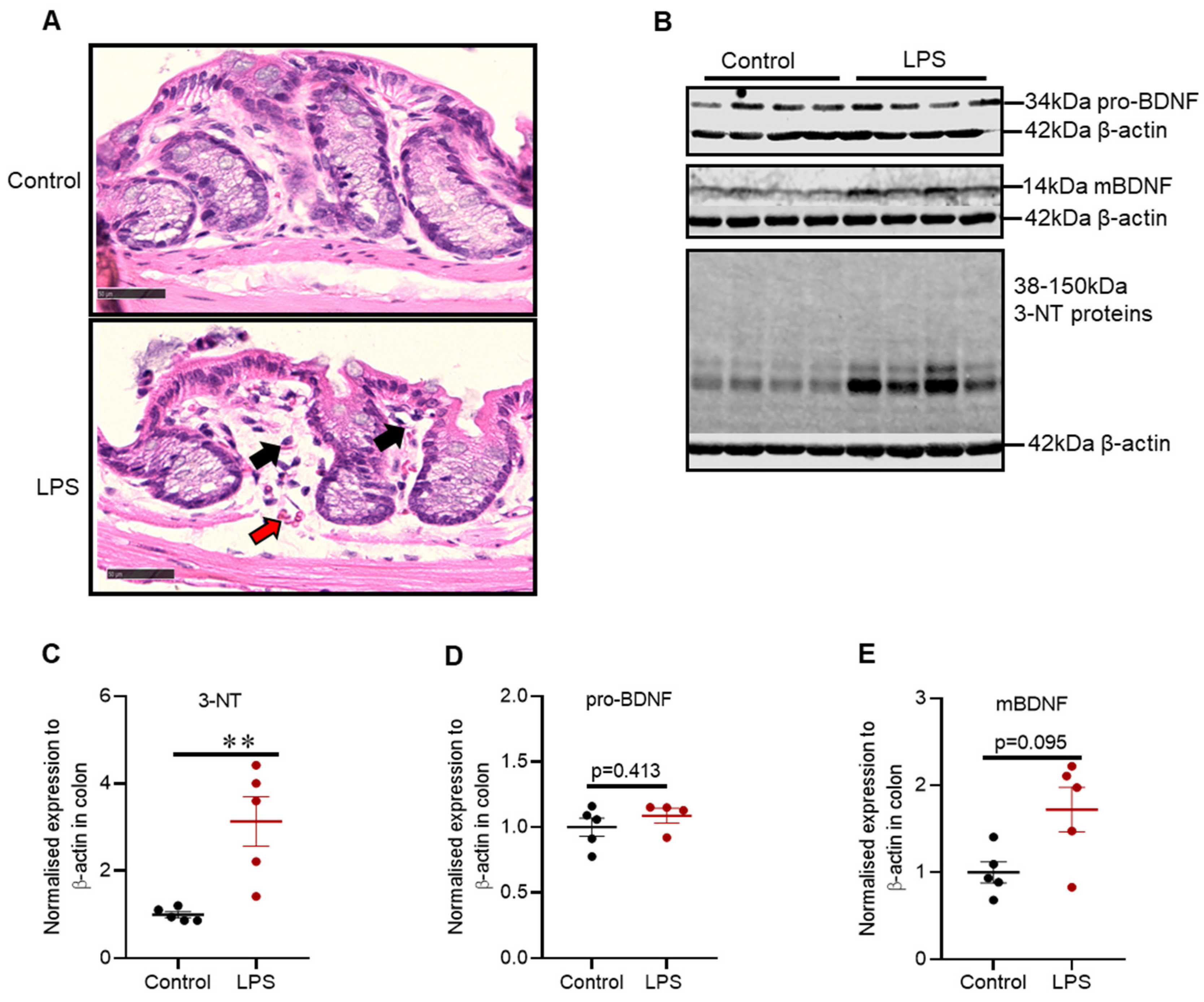
Protective effects of DL‑3‑n‑butylphthalide in the lipopolysaccharide‑induced mouse model of Parkinson's disease
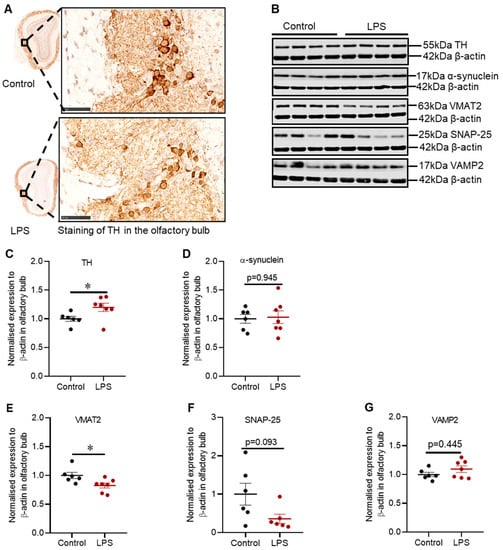
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Further Characterization of Intrastriatal Lipopolysaccharide Model of Parkinson's Disease in C57BL/6 Mice
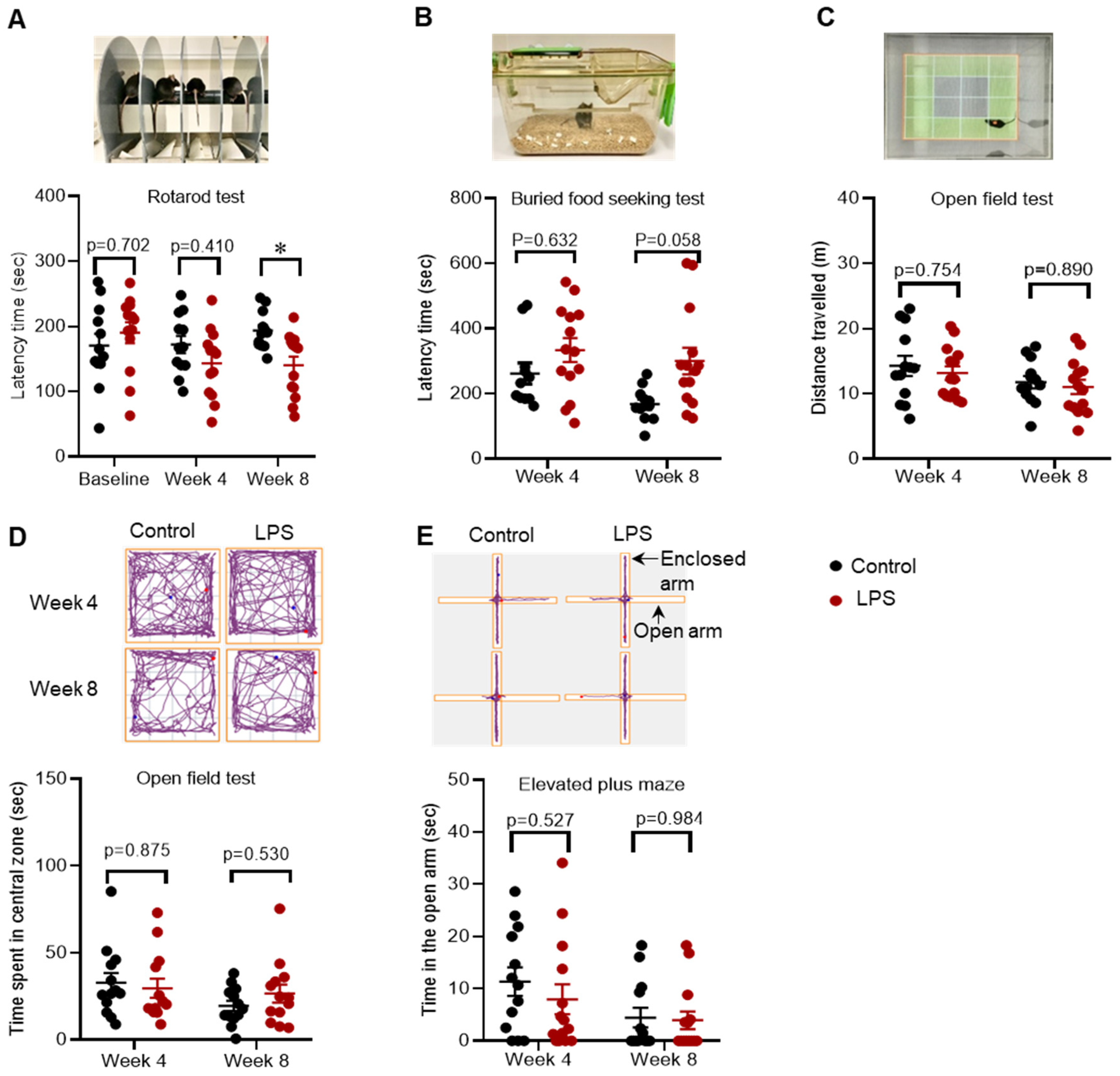
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Further Characterization of Intrastriatal Lipopolysaccharide Model of Parkinson's Disease in C57BL/6 Mice

Lipopolysaccharide animal models of Parkinson's disease: Recent progress and relevance to clinical disease - ScienceDirect
Intranasal LPS-Mediated Parkinson's Model Challenges the Pathogenesis of Nasal Cavity and Environmental Toxins | PLOS ONE
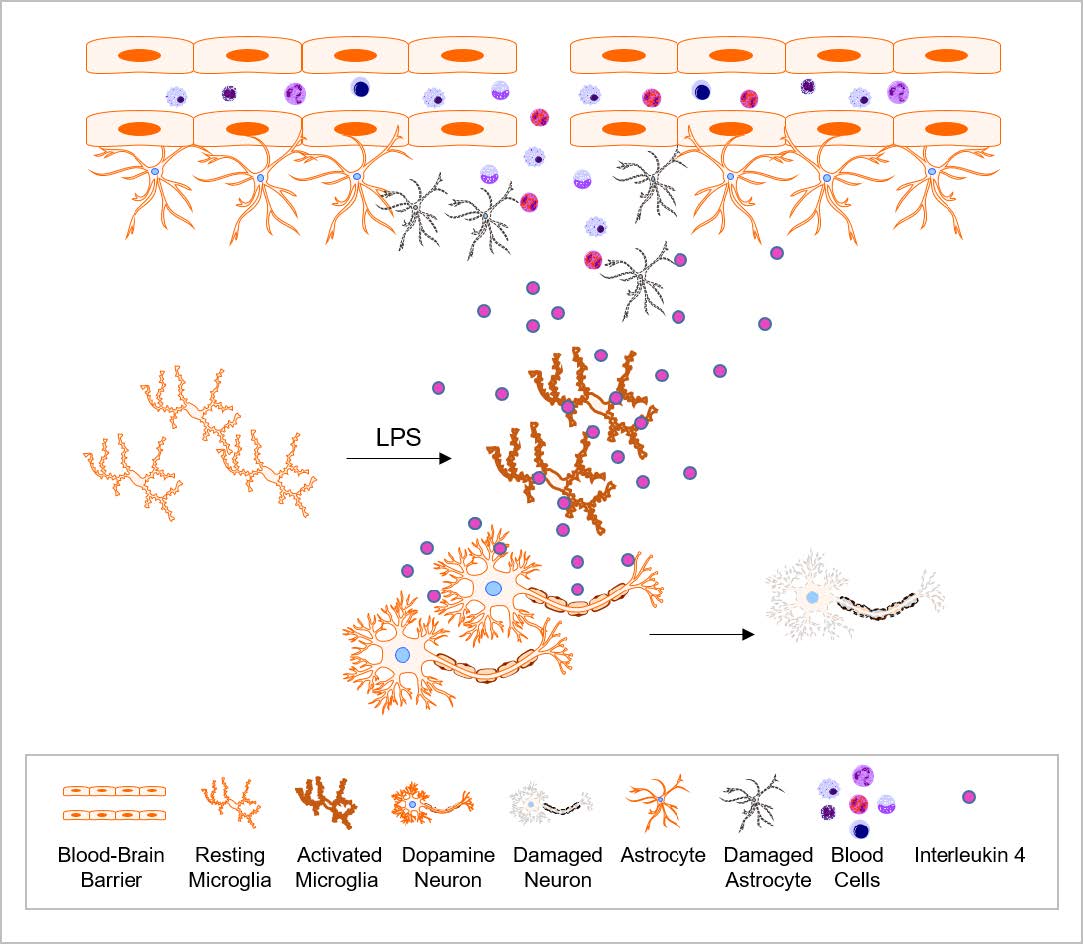
Interleukin-4 Contributes to Degeneration of Dopamine Neurons in the Lipopolysaccharide-treated Substantia Nigra <italic>in vivo</italic>
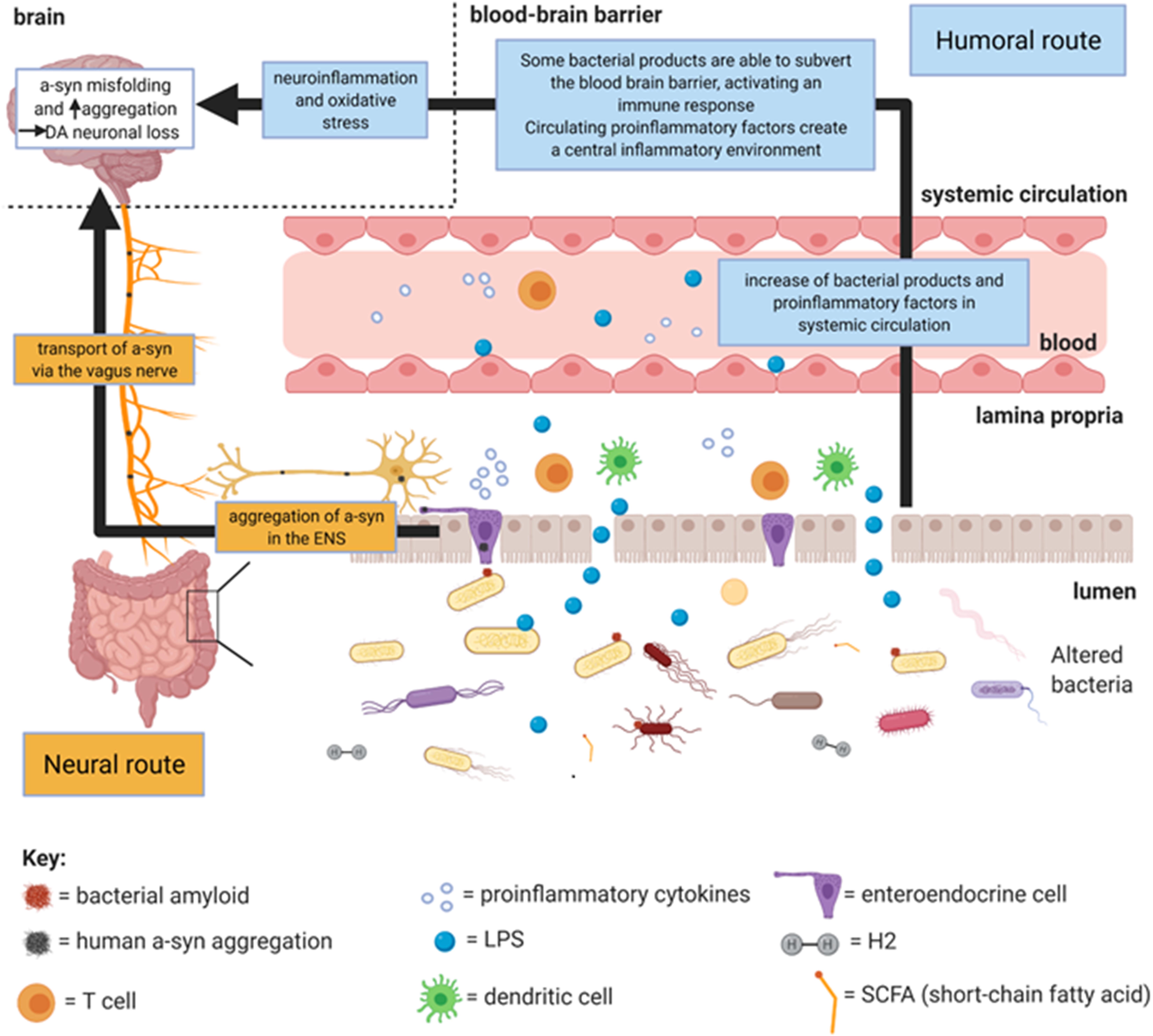
Frontiers | What Is Our Understanding of the Influence of Gut Microbiota on the Pathophysiology of Parkinson's Disease?