Beneficial effect of immunobiotic strains on attenuation of Salmonella induced inflammatory response in human intestinal epithelial cells | PLOS ONE
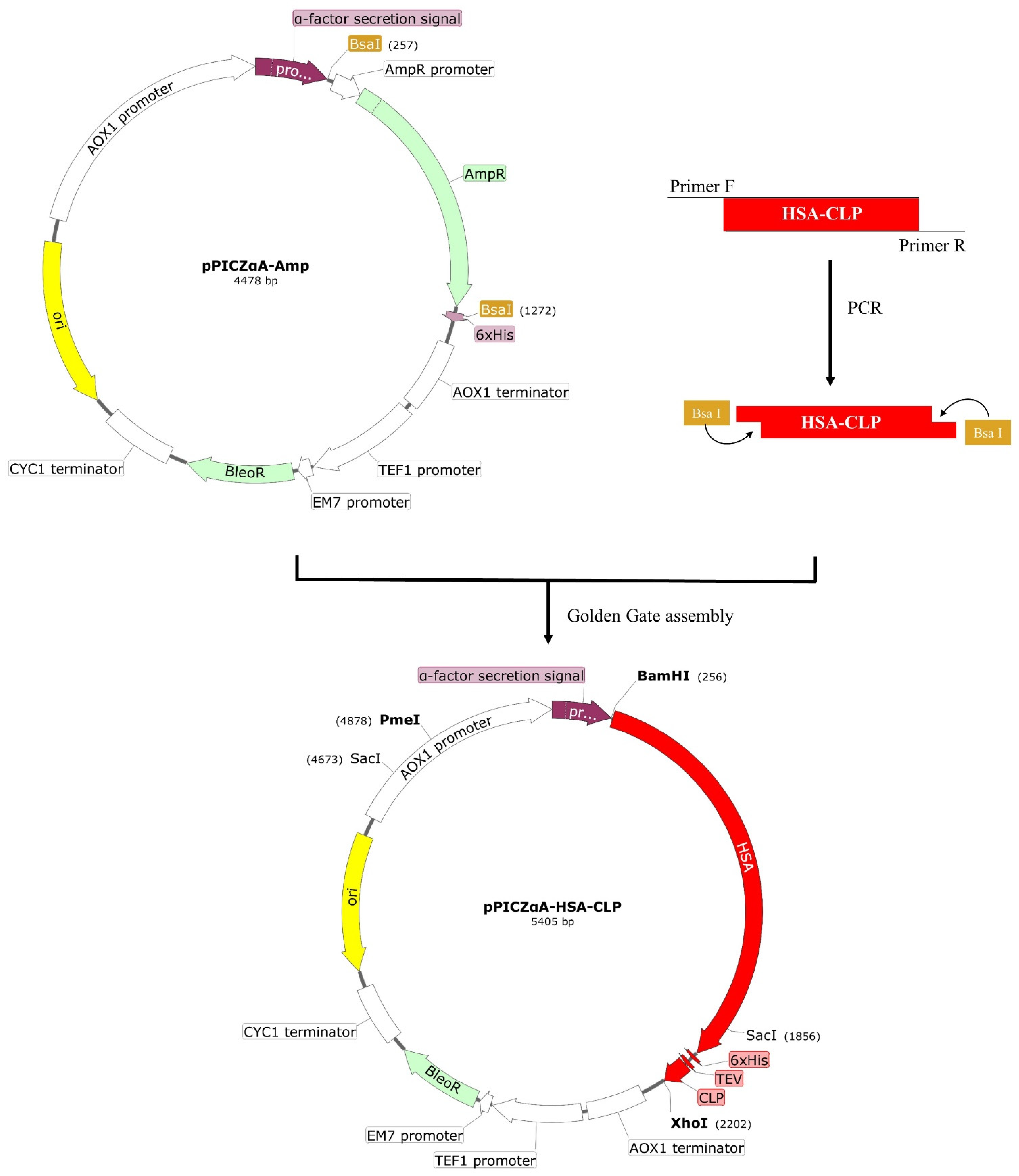
Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Yeast Expressed Hybrid Peptide CLP Abridged Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Levels by Endotoxin Neutralization
Frontiers | Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum Promotes Intestinal Barrier Function by Strengthening the Epithelium and Modulating Gut Microbiota

Surface-Layer Protein from Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation through MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways in RAW264.7 Cells | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Chlorogenic Acid Combined with Lactobacillus plantarum 2142 Reduced LPS-Induced Intestinal Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in IPEC-J2 Cells | PLOS ONE

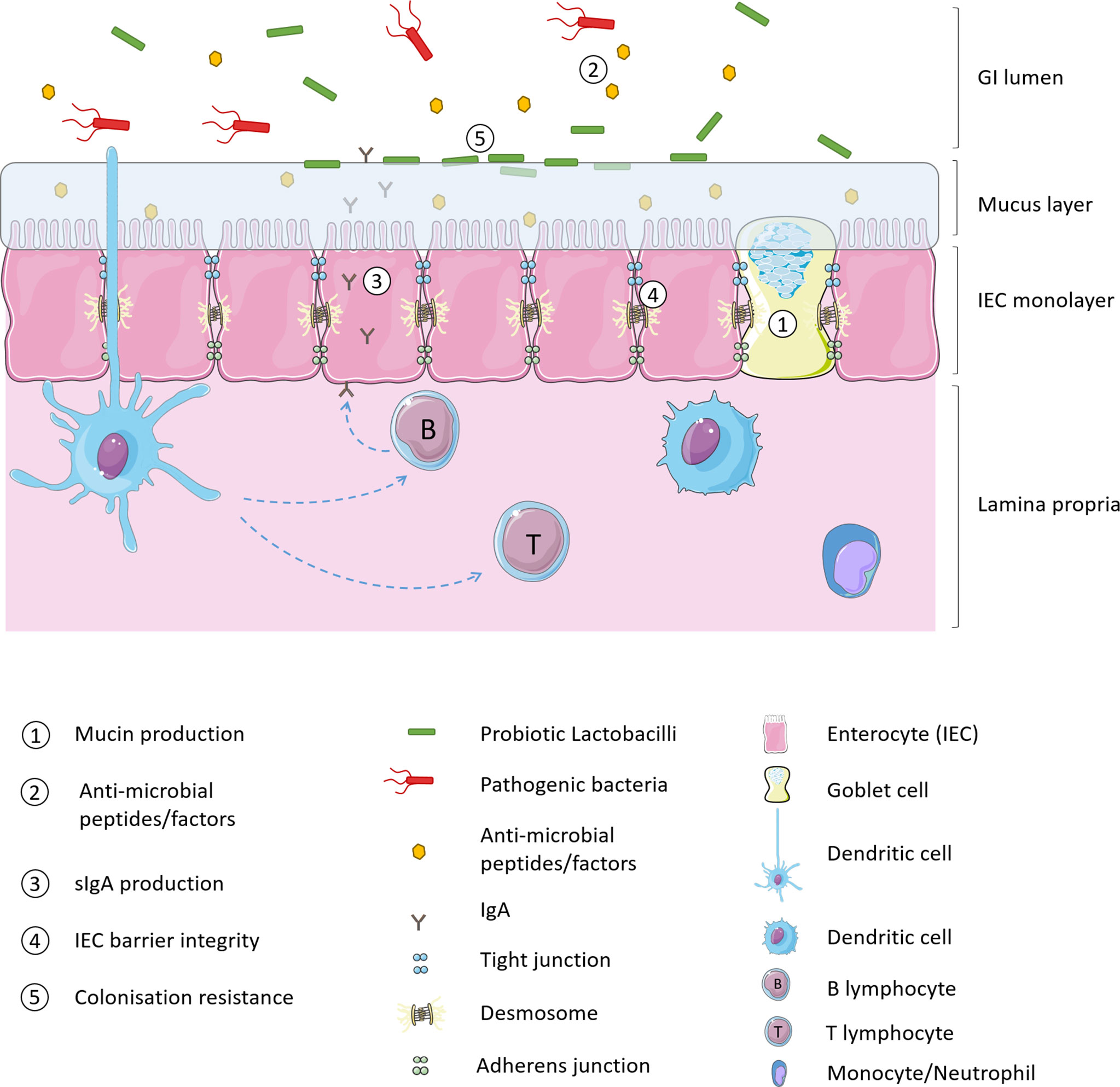
Harnessing the potential of Lactobacillus species for therapeutic delivery at the lumenal-mucosal interface | Future Science OA
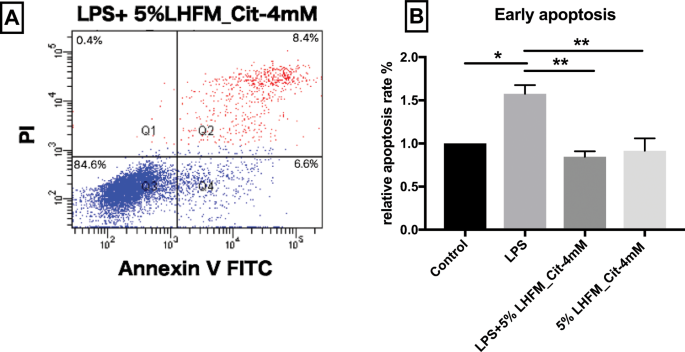
The protective effects of enriched citrulline fermented milk with Lactobacillus helveticus on the intestinal epithelium integrity against Escherichia coli infection | Scientific Reports
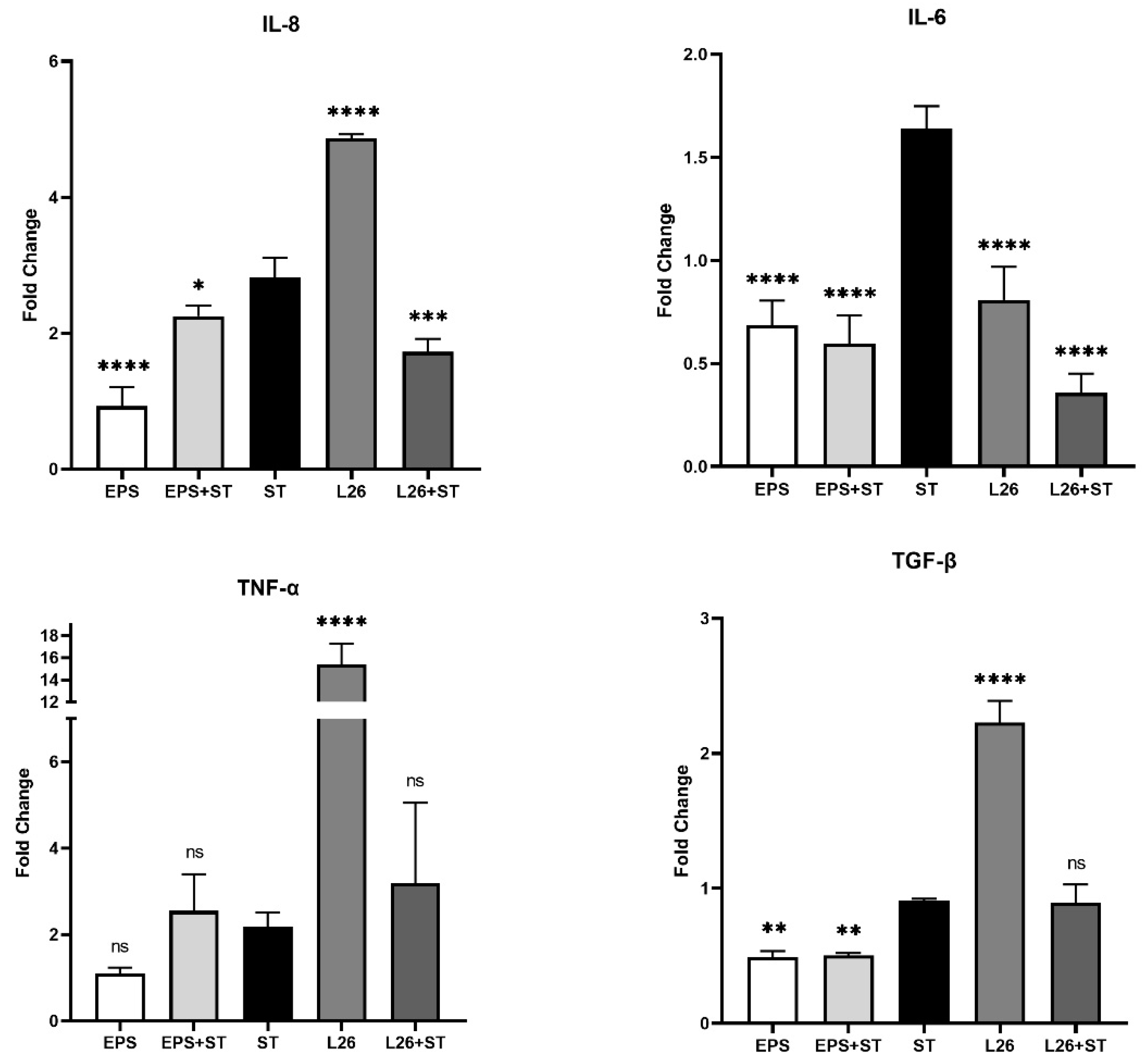
Life | Free Full-Text | Immunomodulatory Effect of Lactobacillus reuteri (Limosilactobacillus reuteri) and Its Exopolysaccharides Investigated on Epithelial Cell Line IPEC-J2 Challenged with Salmonella Typhimurium
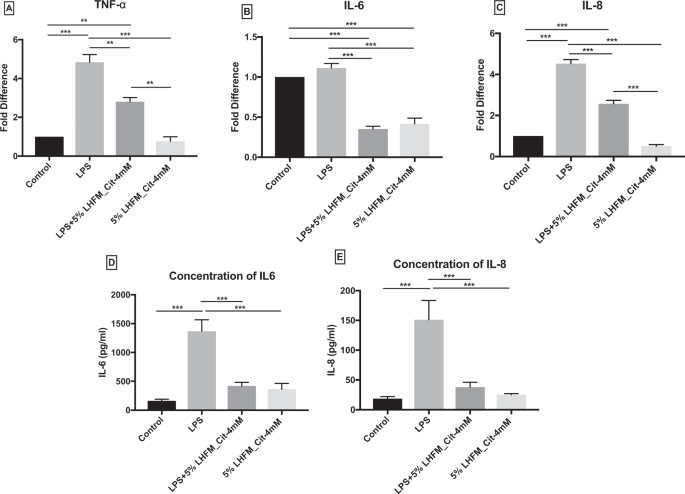
The protective effects of enriched citrulline fermented milk with Lactobacillus helveticus on the intestinal epithelium integrity against Escherichia coli infection | Scientific Reports

Lactobacillus paracasei modulates LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine release by monocyte-macrophages via the up-regulation of negative regulators of NF-kappaB signaling in a TLR2-dependent manner - ScienceDirect
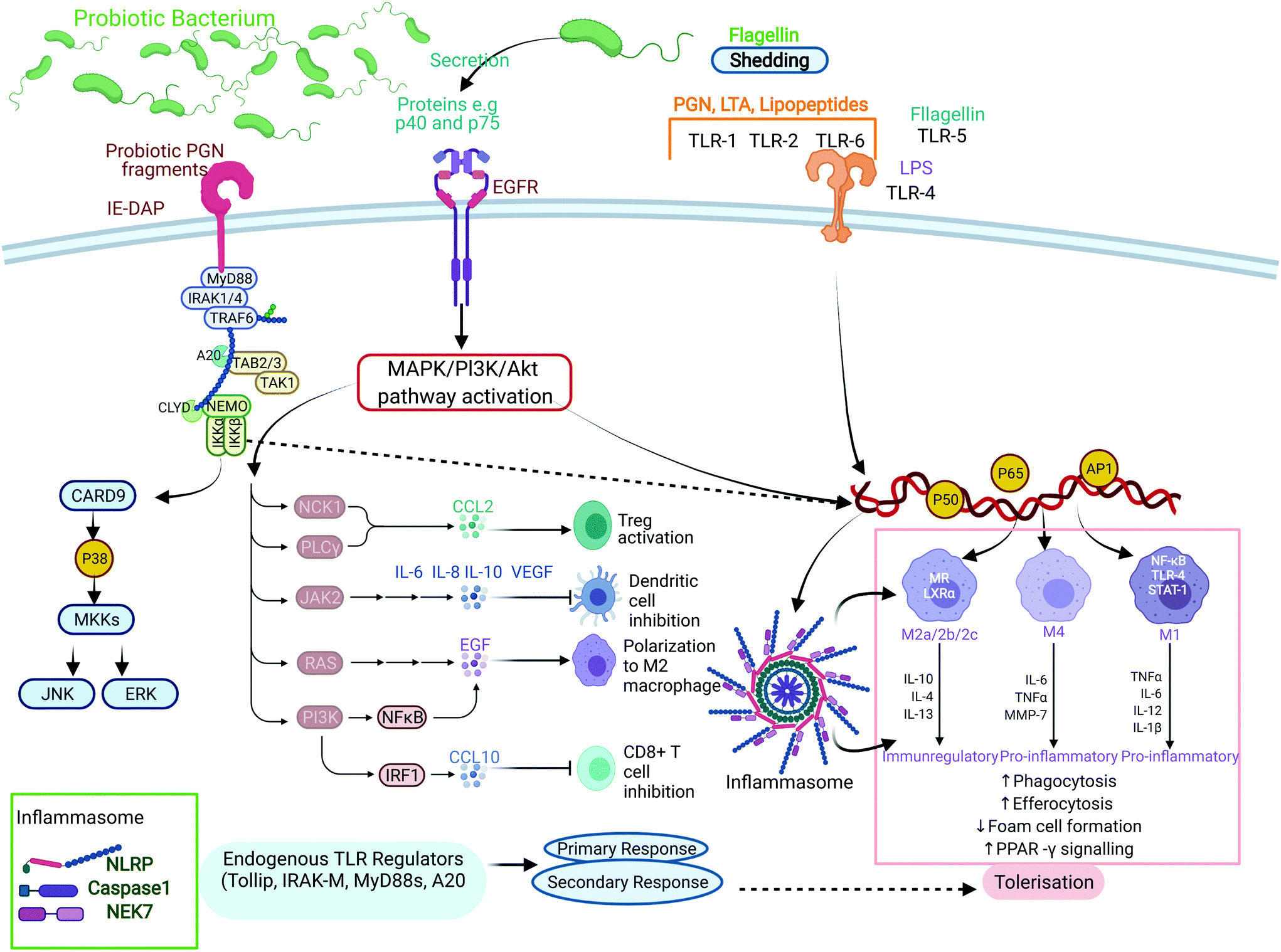
Probiotics and gut microbiota: mechanistic insights into gut immune homeostasis through TLR pathway regulation - Food & Function (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D2FO00911K

The protective effects of enriched citrulline fermented milk with Lactobacillus helveticus on the intestinal epithelium integrity against Escherichia coli infection | Scientific Reports
Effects of (LP) on NF-B pathway Lactobacillus plantarum j activation in... | Download Scientific Diagram
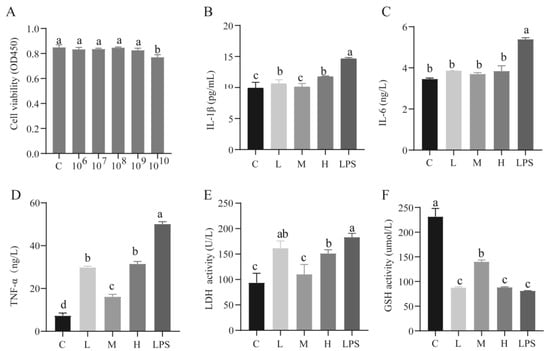
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Lactobacillus rhamnosus CY12 Enhances Intestinal Barrier Function by Regulating Tight Junction Protein Expression, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation Response in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Caco-2 Cells

Immunomodulation and signaling mechanism of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and its components on porcine intestinal epithelial cells stimulated by lipopolysaccharide - ScienceDirect

Metabolites of Lactobacillus plantarum 2142 Prevent Oxidative Stress-Induced Overexpression of Proinflammatory Cytokines in IPEC-J2 Cell Line | SpringerLink

An evaluation of the effects of probiotics on tumoral necrosis factor (TNF-α) signaling and gene expression - ScienceDirect

Anti-inflammatory activities of the selected Lactobacillus strains. A.... | Download Scientific Diagram
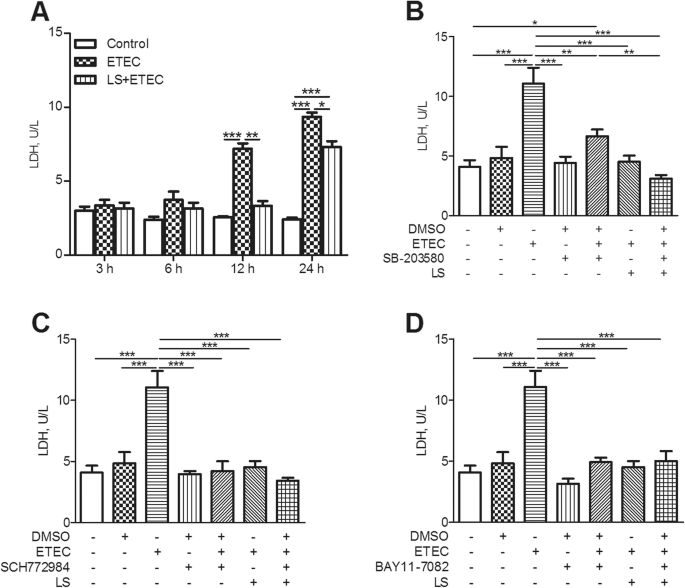
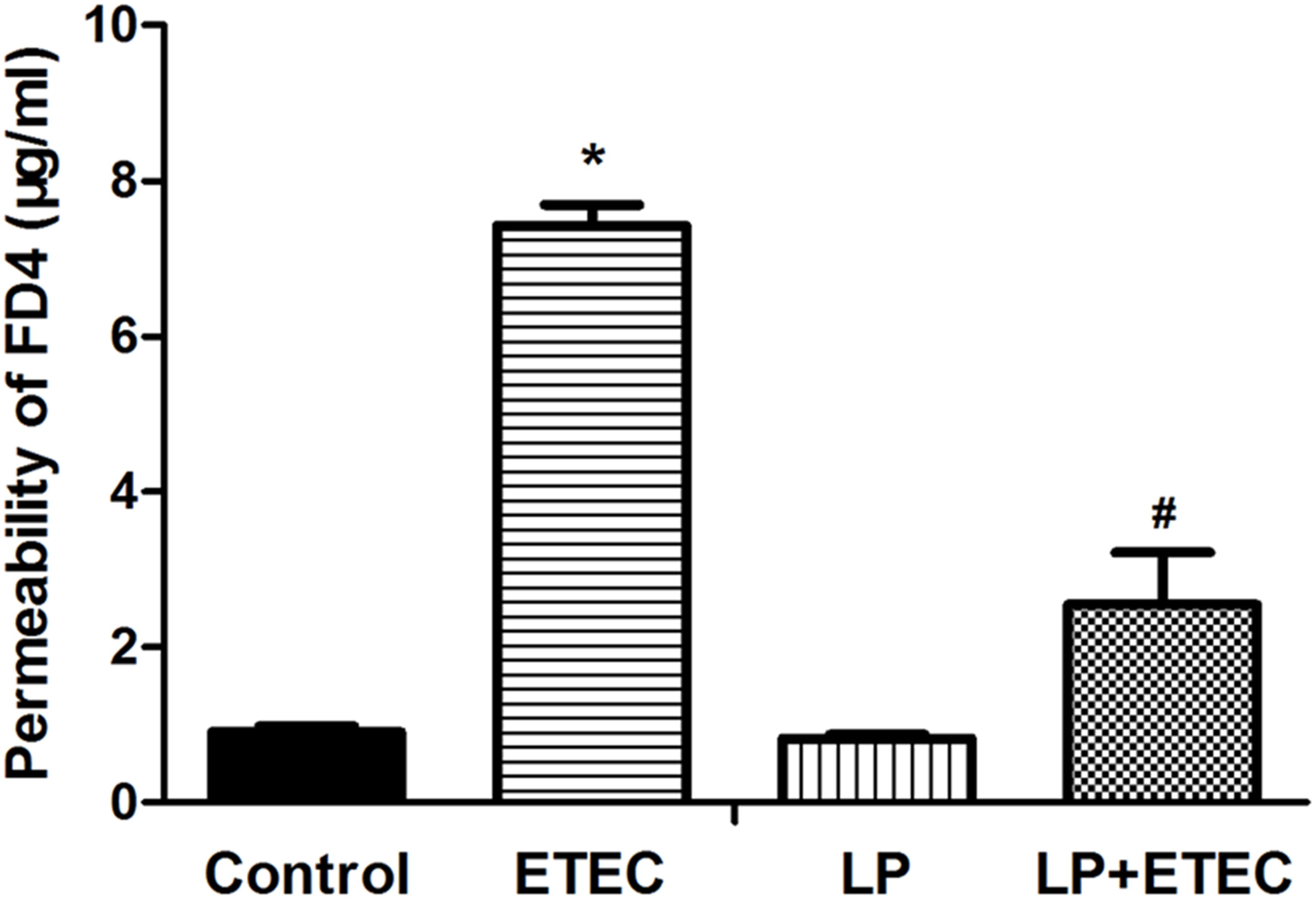
Lactobacillus salivarius alleviates inflammation via NF-κB signaling in ETEC K88-induced IPEC-J2 cells | Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology | Full Text
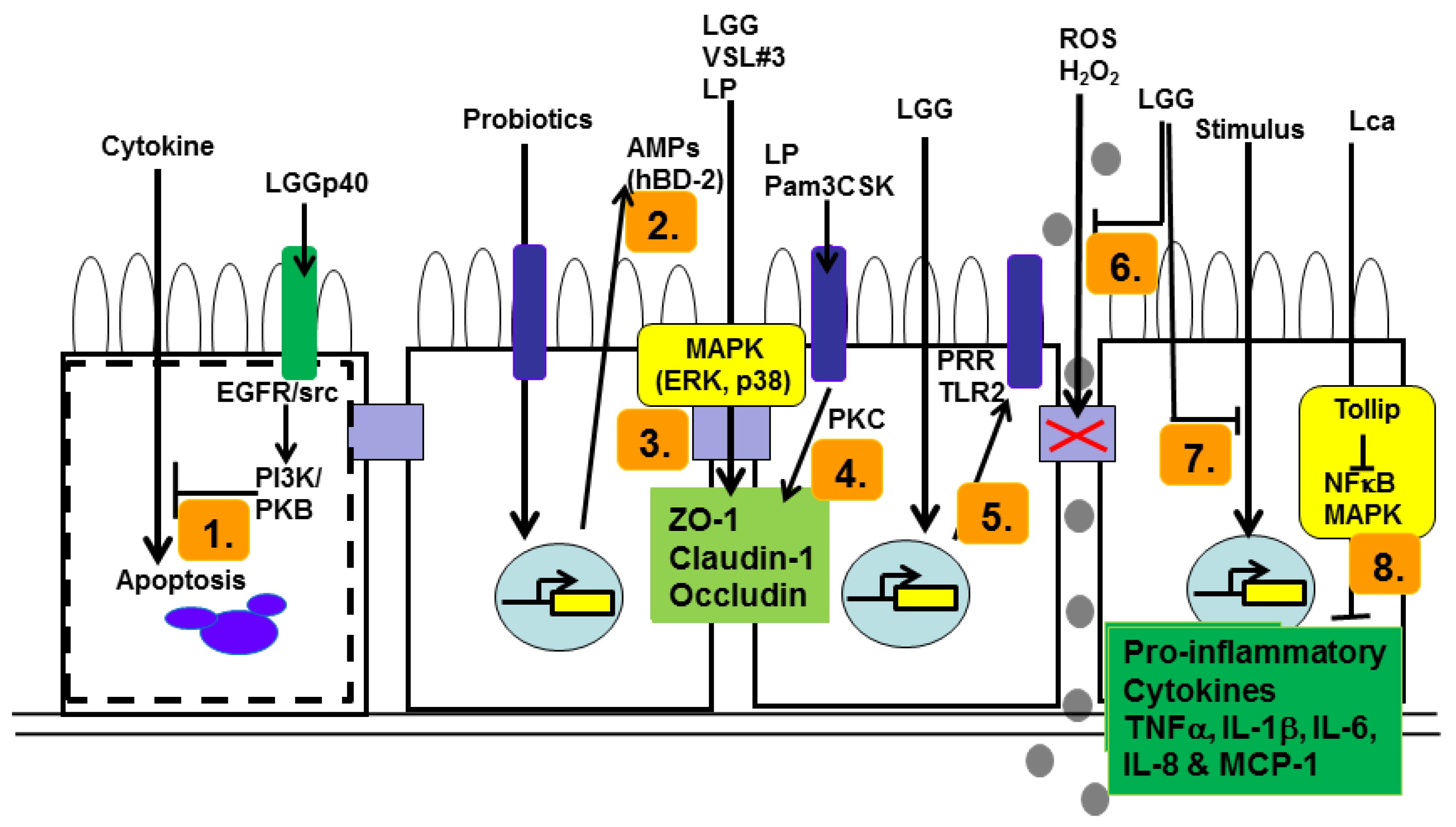
Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Probiotic Modulation of Innate Cell Pathogen Sensing and Signaling Events

Impact of prebiotics on immune response: from the bench to the clinic - Pujari - 2021 - Immunology & Cell Biology - Wiley Online Library

Human-derived probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri strains differentially reduce intestinal inflammation. - Abstract - Europe PMC
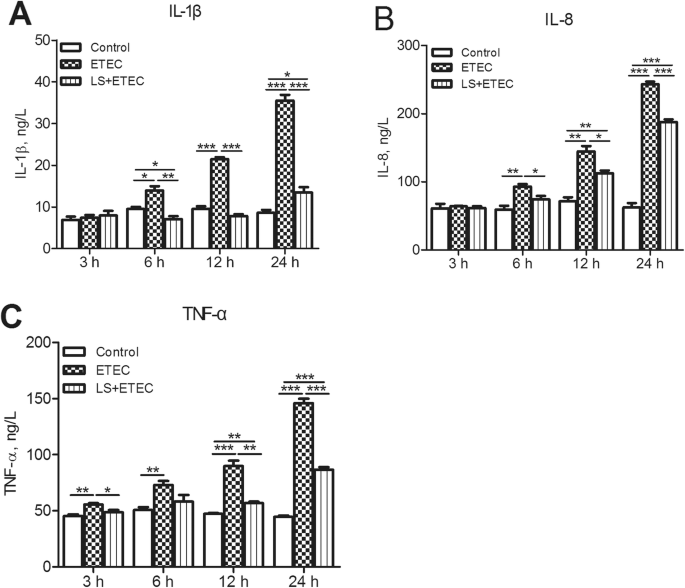
Lactobacillus salivarius alleviates inflammation via NF-κB signaling in ETEC K88-induced IPEC-J2 cells | Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology | Full Text